What is a WMS in Logistics?
What is a WMS and what is it for?
A WMS (Warehouse Management System) allows you to control and optimize, comprehensively, all operations and processes within a warehouse.
Thanks to a WMS, you can automate and synchronize all operations in real time and integrate it robustly with ERP and MES systems to obtain a complete solution connected to production processes.
Whether you are an SME or a large company, a WMS helps increase efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance overall data security in the warehouse and production.
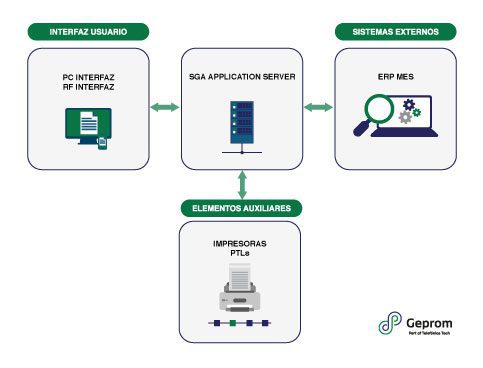
What is a WMS, an ERP, and an MES System?
A WMS (Warehouse Management System) is an essential tool in a warehouse as it helps manage, control, and optimize all operations and processes within the warehouse.
An MES system (Manufacturing Execution System) is software that allows planning, monitoring, and controlling production processes in factories to improve efficiency, quality, and reduce costs.
It is also a valuable tool for an overall analysis of production management, as it can be integrated with an ERP or a WMS.
An ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) primarily records the entire process of a company, of which only part is production. It centralizes information related to accounting, invoicing, human resources, procurement, etc., on a single platform.
ERP systems provide a global view of the business and help improve corporate management. Thanks to ERP, decision-making that directly impacts business management becomes easier.
Key Differences Between MES, ERP, and WMS
An ERP controls all business management processes but is not dedicated to factory production management. For that, there is the MES system, software that regulates and optimizes plant processes.
ERP and MES are continuously communicating and integrated. The detailed production data—machines, quality, etc.—reside primarily in the MES.
Similarly, MES works with ERP and must align with WMS to ensure security and control of warehouse materials. A WMS is the foundation for managing all production components and communicates with an MES to supply production lines.
The MES occupies an intermediate layer between the ERP and the production plant and operates at the same level as the WMS.
Advantages of WMS vs ERP:
A WMS is specifically designed to manage and optimize warehouse operations, whereas an ERP is a broader software solution that can manage multiple business processes, including finance, human resources, customer management, and supply chain, including warehouse operations.
Some advantages of using a WMS over an ERP for managing an industrial warehouse:
- Improved inventory accuracy: A WMS provides real-time visibility of inventory levels, locations, and movements, ensuring accurate counts and reducing stockouts or overstocking.
- Better order fulfillment: A WMS improves order picking accuracy, reduces order cycle times, and increases on-time delivery rates. It optimizes warehouse processes and automates tasks such as order picking and packing.
- Optimized receiving and storage: A WMS automatically assigns incoming inventory to the correct location based on predefined rules, reducing errors and speeding up storage.
- Increased labor productivity: A WMS provides workers with clear instructions on tasks and locations, reducing task completion time and minimizing errors.
- Integration with other systems: While an ERP manages multiple business processes, a WMS specifically manages warehouse operations and can integrate with transportation management systems to provide end-to-end supply chain visibility and control.
In general, a WMS offers more focused functionality and better visibility and control over warehouse operations, making it a more efficient and effective solution for managing an industrial warehouse.
Basic Functions of a WMS:
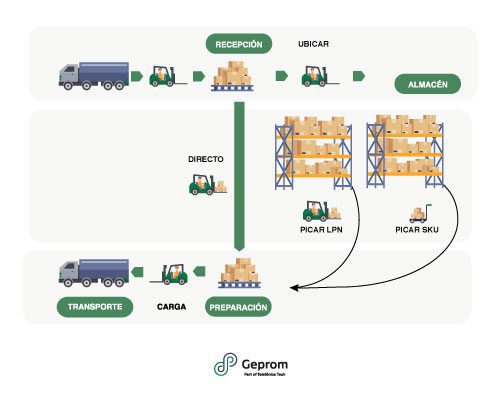
- Inbound management: Receiving goods, collecting logistical data for traceability, labeling, and including quality criteria. Communicates with ERP for administrative management with suppliers.
- Location management: Optimal placement of load units based on rotation, cross-docking, and movement reduction.
- Stock control management: Warehouse map visualization, location management, stock management, item rotation, counting, and inventory.
- Outbound control management: Order preparation, picking process management, labeling and shipping documentation, loading, and ERP communication.
Benefits of a WMS:
- Manage, control, and optimize all warehouse operations comprehensively.
- Real-time inventory visibility and location of factory components (raw materials, auxiliary materials, semi-finished and finished products).
- Traceability of product movements in the factory.
- Optimization of material movements within the plant.
- Management of logistical tasks assigned to operators.
- Management of raw material reception, production cycle, and finished product dispatch.
- Real-time location and stock management.
- Order management through picking tasks.
- Overall data security in the warehouse and production in real time.
- Cost reduction and error minimization.
- Integration with external systems like ERP and MES.
Features of a WMS:
- Flexible, Scalable, and Modular: Adaptable and grows with you.
- Technological connectivity: ERP, RF, RFID, PICKING.
- 100% Logistics: Analytical and operational efficiency.
- Intuitive: Easy to learn and use.
- Integration with ERP and MES systems.
At Geprom | Part of Telefónica Tech, we offer integration of the WMS – Warehouse Management System.
Interested in managing and optimizing warehouse operations?
Contact us to advise you on how to efficiently implement a digital transformation.